Reproductive system of human
It is a natural
phenomenon by which organism reproduce young ones of their own kinds for continuation of race. Human
beings are unisexual or dioecious i.e. male and female reproductive system is
separated in separate individual.
Male reproductive organs
1. Testes
(one pair)
2. Epididymis
(one pair)
3. Vasa
deferens (one pair)
4. Ejaculatory
duct (one pair)
5. Urethra.
6. Penis.
7. Accessory
glands.
 |
| fig:male reproductive organs |
1. Testes: These
are pinkish-oval lie inside the scrotum. The scrotum lies outside the abdominal
cavity. So that temperature of testes remains 2.30c below than
temperature of body. Which is needed to produces sperm.
i. Microscopic structure: There are three layers to cover testis. These are
Outer-tunica vaginalis, Middle-tunica albugania and Inner-layer-tunica
vasculosa.
 |
| fig:T.S. of testis |
fig;
T.S. of testis
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/reproduction-in-animals/human--testis-top-section.jpeg
There are 200-300 testicular
lobules in testis. Each lobule is composed of 1 to 4 coiled seminiferous tubules.
The tubules are lined with germinal epithelial cells (spermatogonia).These
epithelial cells produce sperms by the process of spermatogenesis. Sertoli
cells supply nourishment to develop sperms.
There are interstitial cells
(cells of leydig) in between seminiferous tubules and connective tissue. The
interstitial cells produce androgens, which promotes development of male
accessory glands and controls male sex features (moustache, beard, change of
voice)
ii. Epididymis: it is funnel like convoluted about 6 meters long tube. Board part of
anterior epididymis is called caput epididymis. Middle narrow part is corpus
epididymis posterior end is cauda epididymis.
Function:
store the sperm and secrets fluid to nourish sperm.
iii. Vasa deferens: It arises from cauda. It forms a loop around urinary bladder and joins
with duct of seminal vesicle. It form ejaculatory duct with seminal vesicle.
Function:
carry sperm from testis to seminal vesicles.
iii. ejaculatory duct: There are two short formed by the
union of duct from a seminal vesicle and vasa deferens, there carry the mixture
of sperm and secretion of seminal vesicle.
v. Urethra: it
is 20 cm long arises from urinary bladder. It discharges urine and semen both.
vi. Penis: it
is copulatory organ of human. It is made up of three columns of spongy tissues (two
dorsal cavernosa and one ventral corpora spongiosum). Enlarged-tip of penis is
called glans penis which is highly sensitive. Penis deposits the semen in
vagina with spermatozoa.
vii. Accessory glands:
a. Seminal
vesicles: these are two pouches like
below-posteriorly of urinary bladder and opens into ejaculatory duct. These secret and expel a viscous
fluid which keep sperms alive.
b. Prostate
gland: It lies behind urinary
bladder. It is secretes thin milky substance occupy about 30% volume of semen.
c. Cowper’s
glands: The paired glands lie below
the prostate glands. Their alkaline secretion lubricates the semen flow.
d. Eretion
of penis: Erection is caused by
dilation of blood vessel of blood vessel resulting collection of more blood
spaces of spongy tissue. About 3ml of semen is discharged by penis in each
ejaculation during copulation.
Female
reproductive organs
 |
| FIG: female reproductive organs |
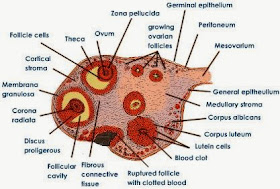
1. Ovaries:
There is one pair of about 3.5cm
long, pink, almond shaped and situated in abdominal cavity on either side
of vertebral column. Each kidney is attached with ovarian ligament and body
wall with mesovarian fold with ovaries. Internally each ovary is differentiate
with
i. Outer germinal epithelium (cubical)
ii. Tunica albunginea: connective tissue below germinal epithelium.
iii. Stroma: Inner mass of
connective tissues made up of cortex medulla.
When Graafian
follicle liberates ovum it is called corpus luteum. The corpus luteum secrete
progesterone hormone in the influence of luteinizing hormone. The hormones
thicken the endometrium wall and activate the mammary gland for their
development.
2.
Fallopian tubes (oviducts): these are
ciliated tubes of 10-20cm long arise from uterus.
It has four parts:
a. Funnel
like infundibulum near ovary with finger like structure fimbriae
b. Wide curved
part ampulla.
c. Narrow
part isthmus.
d. Part near
uterus (uterine).
3.
Uterus: it is a pear shaped
hollow muscular organ. Upper dome shaped part is called fundus. Main part is called body of uterus. Lower portion of uterus
is called cervix.
4. Vagina: It is female copulatory organ. It is tubular, about
10cm long. It passage for menstrual flow and receptor of spermatozoa. In
virgins the vaginal orifice is partially covered by hymen membrane.
5. Vulva: It is external genitalia it is consists of mons pubis
(hair part) clitoris (erectile organ) labia major a (inner fold of vulva).
Libia minora have in more number.
6. Accessory
glands: Bartholin’s glands and mammary glands. Bartholin glands are two bean-shaped lie on either of side of
vaginal orifice. These glands secret viscid fluid for lubricant of vulva during sexual
intercourse and sexual excitement.
Mammary glands: these are pair rounded with median nipple. Each gland made up of 15-25 lobules of milky glands. Each gland sends a lactiferous duct toward nipple. Milk gland produce milk under the control of prolactin and ejection of milk is controlled by pituitary gland.
Menstruation (ovarian) cycle: It is cyclic changes occur in reproductive tract of
human female on a period of 28 days. It is confirmed by loss of vaginal blood.
It occurs at about 13 years of age till the age of 50-55 years. The
menstruation is seen in human monkeys, gorilla etc.
The menstrual cycle is categorized into three phases
A. Menstrual
phase; it is the phase of blood
flow. It last for 3-5 days. It is caused due to cast off epithelia lining of
endometrium. Oestrogen and progesterone is very law in the blood. Menstruation
is observed only when ovum remains unfertilized.
B. Proliferative
or follicle phase:
i. Number of
endometrium phase. It is last of endometrium in the phase. It last for 9-10
days( 5th -14th ) day.
ii. The release of FSH from pituitary stimulates
the development of follicles of ovary.
iii.
Ovarian follicle
matured into griffin follicle and secrete oestrogen hormone which increases up
to 12th days.
iv.
Oestrogen
enhances proliferation of cells of endometrium of uterus and fallopian tubes (up
to 2-3mm thickens). The wall is highly supply with blood vessels and ready for
implantation.
C. Secretory or
luteal or ovulatory phase
i.
It last for about
12-14 days (14th- 28th day of menstrual cycle).
ii.
LH (lutening
hormone) is secreted by pituitary gland called luteal phase.
iii.
LH and FSH
stimulate the ovulation (releases of ova).so that LH and FSH concentration
become high at this time.
iv.
After ovulation
follicles of ova (corpus luteum) secret progesterone hormone.
v.
Progesterone inhabits maturation of any
follicle and ovulation.
vi.
Progesterone
stimulates thickening of endometrium for implantation of zygote. It also
stimulates to secret water mucus and also affects mammary glands.
What is menopause?
It is
phase of women’s life. It occurs between 50 to 55 years. At that age ovaries
are less responsive to FSH and LH. Ovulation and menstrual cycle becomes
irregular and stop. After the menopause female loses the ability to reproduce
progesterone and oestrogen hormone becomes imbalance.
If
ovum is not fertilized
|
If
ovum is fertilized.
|
|
|


Well explained. Thumbs up to you. Thank you so much for sharing this information. IVF Center in India has played a major key role in removing the infertility problem.
ReplyDeleteyou shared really nice information regarding Reproductive systems of male and female. to know more about reproductive surgeries you can contact Dr. Neelu Test Tube Baby Centre.
ReplyDeleteThank you for sharing such wonderful information!In my opinion, Keep a healthy life by consuming healthy food and doing exercise regularly is the best diet formula.
ReplyDeleteMedical Jobs